The evolving structure of a scientific citation network and its political effects
Current literature describes tutorial quotation networks and the construction of information fields: their numerous patterns, clustering, fragmentation, structural cohesiveness, and the hyperlink between micro and macro degree processes in rising domains of scientific data manufacturing (Small & Griffith, 1974; Hill & Carley, 1999; Gondal, 2011; Daipha, 2001). Nonetheless, little has been written to explain the precise structural adjustments over time of quotation networks. How do sure nodes emerge and grow to be central or structurally essential over time? How and why do different nodes, essential early within the quotation community’s evolution, grow to be far much less essential because the community matures? What are the macro and micro degree processes that describe and govern this habits and what social, epistemological, and political classes can we draw from these adjustments?
These questions are essential for rising our theoretical understanding of evolving scientific domains of information. Virtually, these questions are additionally essential to discover the biopolitical dimensions of evolving hegemonic scientific domains and the constraints they place on practitioners making use of domains of scientific data. A central notion within the sociology of well being and drugs is the social building of sickness. Illness, illness, and well being issues are concurrently materially positioned organic phenomena and a socially created which means making processes by way of which normalcy and deviance get outlined and play out in socially related shows of energy and inequality. Some sicknesses are significantly embedded with cultural which means, others are socially constructed on the particular person degree–based mostly on how people come to know and reside with their sickness. Others are particularly formed by technical medical and scientific data and should not essentially given by nature however are primarily constructed and developed by claims-makers and events (Conrad & Barker, 2010).
Moreover, the method of medicalization—the tendency to inscribe increasingly social issues to be inside the skilled area of medication—continues to be a dominant pattern in society. By increasing the medical area to ever extra points and social issues, the challenges and conflicts related to naming and framing sickness involves the fore. Somewhat than a given biomedical reality, we now have a set of understandings, relationships, and actions which are formed by numerous sorts of information, expertise, and energy relations, and which are continually in flux. This social constructionist perspective seems to be at how the phenomenon was recognized and acted upon. Analysis is a matter of the “politics of definitions” (Brown, 1995).
Although medical sociology has given nice consideration to the complexities and power-processes related to naming, diagnosing, and constructing techniques to look after illnesses on the inhabitants degree, much less consideration has been paid to the ways in which the construction of educational literature, and the quotation networks that symbolize them, contributes to the processes of naming, framing and governing of sickness. This paper seems to be on the structural evolution of the educational literature that offers with the intersection of noncommunicable illnesses and “international well being.” Traditionally and at the moment, each the phrases “international well being” and “noncommunicable illnesses” (hereafter, NCDs) have been hotly contested (Airhihenbuwa et al., 2014; Whyte, 2012; Fassin, 2012; Beaglehole & Bonita, 2010). Each the broad and diffuse idea of “international well being” and seemingly technical and clinically delimited subject of noncommunicable illnesses show the methods wherein medical and scientific data is socially constructed in advanced methods (Keane, 1998; Brown, 1995; Lantz & Sales space, 1998). The framing of NCDs within the international coverage literature, specifically, has been a battle floor of biopolitics (Bukhman et al., 2015; Binagwaho et al., 2014; Katz, 2013; Mamudu et al., 2011).
Constructing off the present literature, I visually look at the altering construction of the worldwide well being / NCD tutorial literature quotation community in addition to quantitatively discover the adjustments in a few of the macro-level traits of the quotation community and their adjustments between 1995 and 2016. Moreover, utilizing ERGM methods, I additionally discover proof in assist of essential adjustments within the density and the emergence of a small variety of structurally essential paper / nodes within the community.
To conclude this paper, I’ll discover how structural adjustments on this quotation community correspond with the content material of the papers that dramatically change their structural place inside the community. By linking this to a historic understanding of the altering framing of NCDs within the international coverage making area, I hope to make the argument that structural adjustments within the NCD/international well being quotation community formed the framing for and contributed to limiting the political alternatives accessible to activists searching for to mobilize new assets for the rising NCD burden amongst low earnings populations globally.
2) Analysis Query
Extra concretely, I hope to reply the next questions: 1) How do the worldwide traits of the NCD/ international well being quotation community change, qualitatively and quantitatively, between 1995 and 2016? 2) What have been crucial micro-level buildings that precipitated macro-level adjustments within the community over that point interval? What historic, social, and political results might these structural adjustments within the community each symbolize and maybe be inflicting within the broader subject of worldwide well being governance?
3) Information and Strategies
Analysis targeted upon the construction of information manufacturing steadily depends on community knowledge (Gondal, 2011). As Gondal describes,
“The nodes within the community could also be researchers, paperwork, ideas, or organizations. The sides connecting these nodes correspondingly are collaborative authorship (Babchuk et al., 1999; Moody, 2004; Goyal et al., 2006), social and mental contacts between scientists (Lievrouw et al., 1987), co-occurrence of references within the bibliographies of different paperwork or co-citation (Small and Griffith, 1974; Moody and Mild, 2006), shared citations of the identical different paperwork or authors often known as bibliographic coupling (Kessler, 1963), sharedmem- bership in organizations (Cappell and Guterbock, 1992; Daipha, 2001), or conceptual similarity between paperwork (Small, 1978; Lievrouw et al., 1987; Hill and Carley, 1999). The evaluation of such networks constructed from quotation indices, organizational memberships, and authorships is basically performed at two ranges. On the dyadic degree, researchers have been involved with the which means attributed to the sides interlinking the nodes. On the ‘international’ or ‘macro’ degree, researchers analyze the topological properties of the community as a complete offering a chicken’s-eye description of the analysis subject. There’s one more degree – the ‘native’ or ‘micro’ degree – involving multiple tie however considerably lower than the entire community which stays comparatively under-analyzed within the literature.”
On this paper I try to indicate not solely the birds eye view of how this quotation community grows and evolves over time, but in addition how the micro-level buildings that trigger ties change evolve over time as properly. I achieved this by constructing a plain .txt quotation knowledge set from Internet of Science (webofknowledge.com) querying the database and downloading all related quotation and paper knowledge for the papers assembly the search standards. My standards for this search have been a) any of the illnesses listed by the Institute for Well being Metrics and Analysis as a “noncommunicable illness” (every with logical ‘or’), AND b) the time period “international well being”, c) between the dates of 1995 and 2016. I then used the CRAN “bibliometrics” package deal, downloaded to RStudio to rework this plain textual content knowledge file into an adjacency matrix (see Appendix 1 for R code). From there, I used to be in a position to generate the annual graphs of the rising NCD / international well being quotation networks and their corresponding betweenness, closeness, and diploma statistics. I moreover used the VOSViewer software program for mac to additional discover the construction and patterning qualitatively for the community. Lastly, utilizing the CRAN ERGM package deal in R, I ran ERGM fashions, testing for the log probability of the presence or absence of assorted essential micro-level buildings which will or is probably not current within the given networks and will or could not change over time. General, this knowledge set give me a helpful view into each the micro and macro degree buildings and patterns inside the international well being / NCD quotation community, nevertheless it additionally provides me good decision as to how these community properties have modified over time.
4) Outcomes
4.1 International Properties of the Community
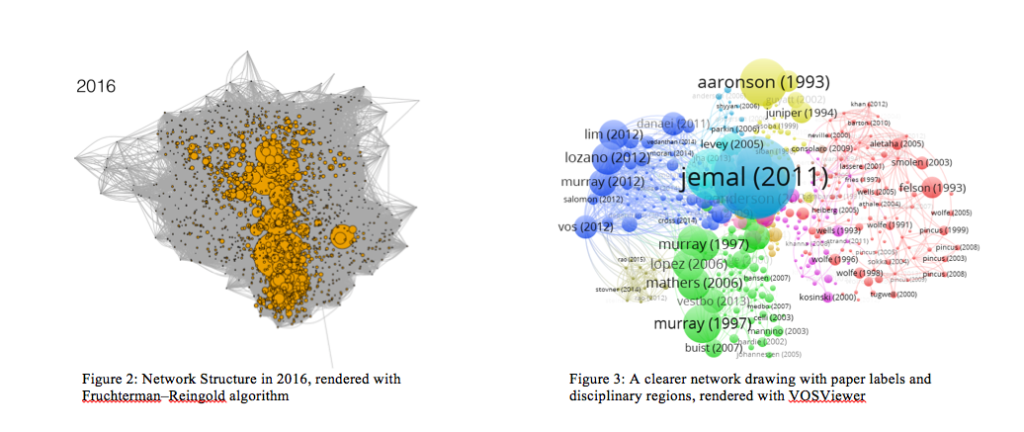
Determine 1 visually exhibits the evolving NCD / international well being quotation community over time, between 1995 and 2016. We see the community going from a mere handful of papers in 1995 to a seemingly very densely packed mess of papers, citations, and nodes in 2016. Nodes are barely expanded based mostly on their diploma quantity (variety of papers citing that paper) and so we see, beginning in about 2001, the emergence of some “key nodes”—or papers that appear to be rising shortly within the variety of citations that they’re receiving from different papers within the community. Beginning at about 2006, we see a big density sample in the direction of the underside of the community graph.These patterns are extra simply visualized within the VOSViewer software program. Utilizing this visualization software program, it’s straightforward to see the breakdown of papers, the authors, their subjects, and the conceptual/subject space/disciplinary clustering. Determine 3 exhibits the outcomes of the visualization of the NCD / international well being quotation community in 2016 by way of the VOSViewer. Right here we see that it has grouped the essential nodes within the community into disciplines / areas of analysis based mostly on the variety of shared citations. The blue area represents papers involved with international psychological well being points. The inexperienced area represents pulmonary illness, coronary heart illness, and epidemiological research targeted on life-style threat elements and inhabitants degree public well being intervention. The pink area has to do with continual ache points, arthritis, and different rheumatic illnesses. Lastly, the yellow area represents papers that must do with numerous types of most cancers. It’s attention-grabbing to notice that papers of comparable subject and medical space are inclined to group collectively.
One other attention-grabbing discovering from this evaluation was the see the speedy progress in significance of huge scale epidemiological modeling and burden of illness measurement papers on the expense of extra medical/intervention targeted papers. Particularly, the papers by Murray, Jemal, and Lozano are all giant scale quantitative epidemiology papers geared toward measuring totally different parts of the noncommunicable illness burden throughout the globe. This corresponds to a few of the different the essential findings by way of altering structural significance inside the community, which we I’ll talk about shortly.
4.2 The Altering Community Over Time
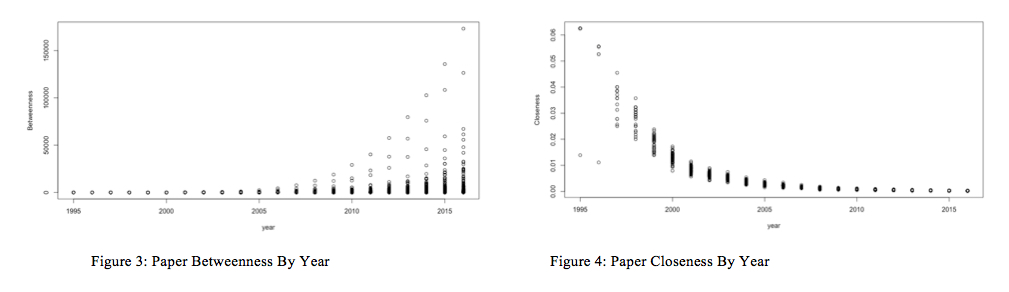
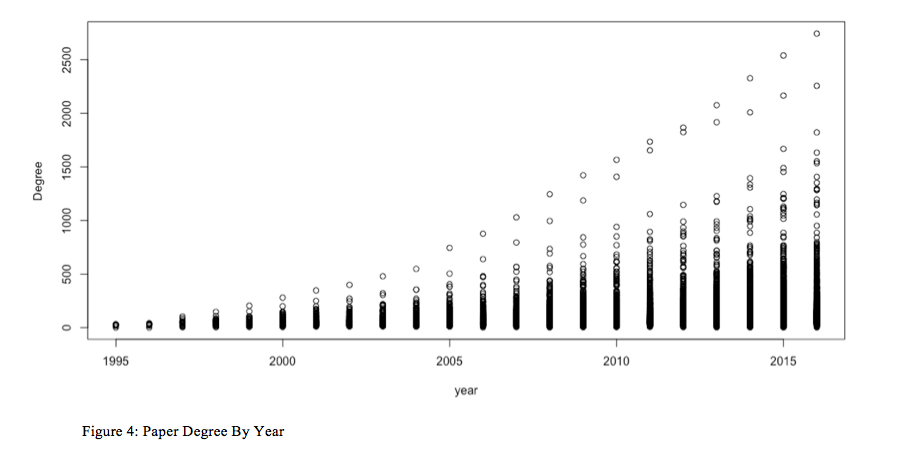
Along with visually seeing the evolution of this quotation community over time, I additionally needed to discover some key community statistics—significantly totally different measures of centrality—of the papers within the community, and the way these modified over the evolution and maturation of the quotation community. Figures 3, 4, and 5 present all the networks papers’ betweenness centrality, closeness centrality, and diploma between 1995 and 2016. Betweenness centrality refers back to the variety of actors that should “cross by way of” a given node with a view to attain different nodes. Extra technically, “if the geodesic between actors n2 and n3 is n2n1n4n3 — that’s, the shortest path between these actors has to go “by way of” two different actors, n1 and n4 — then lets say that the 2 actors contained within the geodesic may need management over the interplay between n2 and n3” (Wasserman & Faust, 1994, p. 188). This “actor within the center” has a point of management over the graph, therefore it is a vital statistic to quantify. Closeness centrality focuses on how shut an actor is to all the opposite actors within the set of actors. The thought is that an actor is central if it will probably shortly work together with all others (Wasserman & Faust, 1994, p. 183). Lastly, diploma merely refers back to the variety of edges related to a given node. On this case diploma is the same as the variety of papers citing a given paper within the community.
Viewing Figures 3, 4, and 5 collectively reveals an attention-grabbing and hanging sample. First, in Determine 3 we see betweenness centrality unfailingly, but unequally rising for all papers within the community. Determine 4 exhibits conversely that paper’s closeness centrality unfailingly decreases over the time interval noticed, however once more at barely totally different charges. Lastly, Determine 4 exhibits that diploma seems to go up for all papers within the community, once more at dramatically totally different charges throughout this quotation community.
These observations show an attention-grabbing conclusion for this community: that betweenness and closeness look like inversely associated to 1 one other over time as a quotation community grows over time. Virtually, what this implies is that as papers proceed to be added to the scientific community area of worldwide well being / NCD analysis, they’re more and more citing seminal papers and making connections with different, much less cited papers within the community. This quickly rising, however comparatively sparsely related community creates increasingly betweenness for every paper—there are extra steps by way of the networks by way of which to go and therefor every paper in these steps are between ever extra papers. However, on the similar time, papers are being added to the community at such a speedy charge (and papers can solely cite so many different papers) that community is changing into more and more much less dense and therefor the closeness of the papers inside the community shrinks dramatically, particularly beginning round 2000. Lastly, it additionally is smart that on the whole, the diploma for papers within the community would develop persistently over the course of the evolution of this quotation community. Papers, even these not often cited, will solely develop of their variety of citations and received’t lower.
Desk 1 (to be mentioned extra beneath) exhibits the variety of papers within the community for annually: there’s an nearly exponential addition of latest papers to the community beginning round 2002. Given this explosion of latest nodes being frequently added to the community, the comparatively few citations anybody paper can have, it is smart that closeness centrality would plummet over the course of the evolution of this community and that betweenness inside the community would improve because the sparsely—but nonetheless fully related—community continues to develop.
4.3 Differential Eigen Centrality Developments
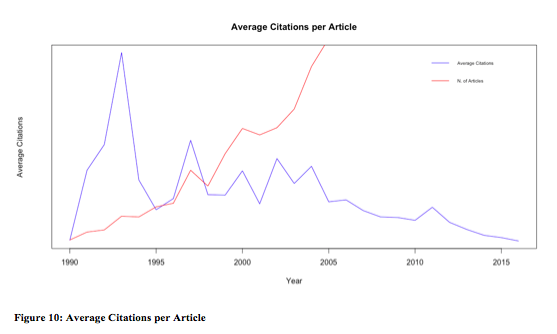
So, over time, the NCD / international well being quotation community appears to each be rising by way of its general dimension, the variety of citations, and therefor its common betweenness of the papers within the community. Conversely, the community is changing into way more sparsely related due to the sheer charge of addition of latest papers and the restricted numbers of citations that every paper could make (see Determine 10). What concerning the significance of explicit papers? Are there particular papers (or teams) that appear to be changing into kind of essential within the community regardless of the speedy enlargement of the community itself?
Eigenvector centrality is one such measure of significance or affect inside a quotation community. It assigns relative scores to all nodes within the community based mostly on the quantity connections and high quality of the scores of the connections a node has. The extra essential the node’s connections, the upper that node’s eigenvector centrality shall be (Newman, 2014). We would hypothesize that much like the betweenness measure, all papers would are inclined to grow to be extra essential inside the community over time. Or, conversely, maybe, eigenvector centrality would are inclined to lower quickly with the speedy improve of the scale of this quotation community. Puzzlingly, neither appears to be the case: Determine 5 appears to indicate that a few of the papers on this quotation community are rising of their eigenvector centrality rating between 1995 and 2016, whereas different papers within the community lower by way of eigenvector centrality over this time interval. How can we account for this?
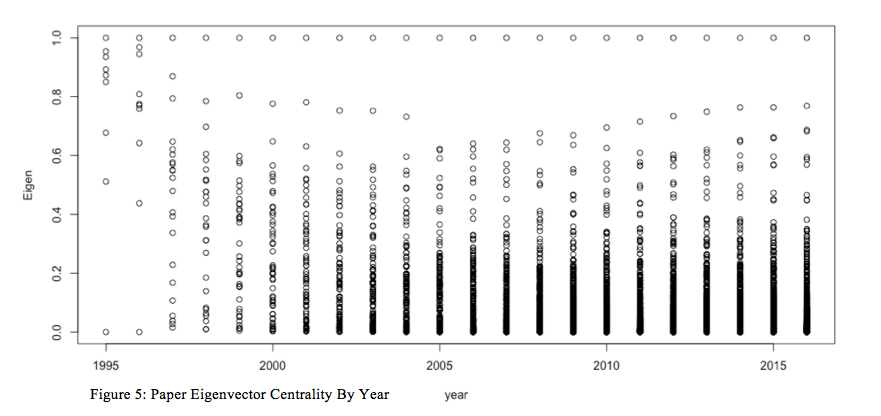
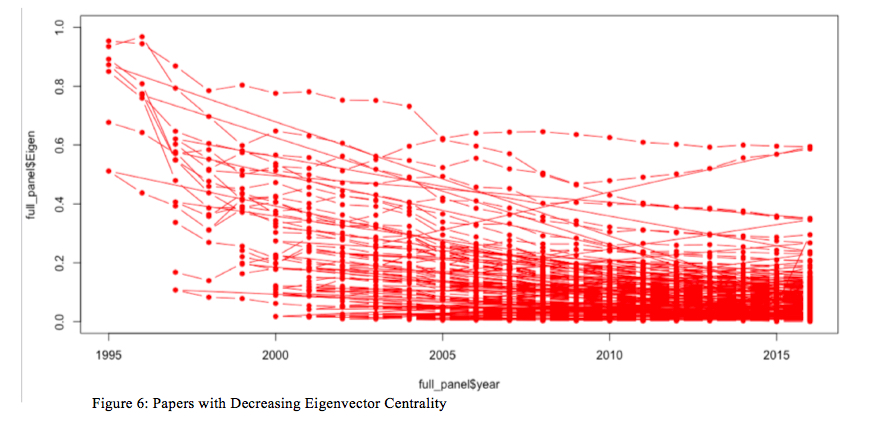
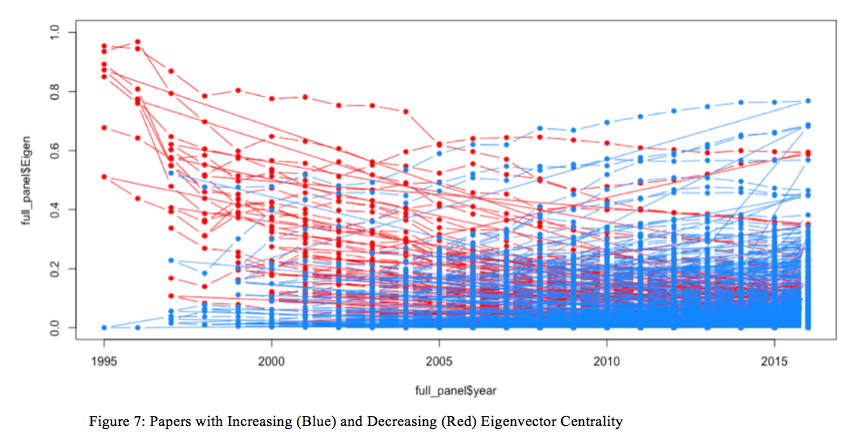

It appears that there’s some sample—some papers improve in eigenvector centrality whereas different papers lower in eigenvector centrality—over the time interval noticed. However, what’s the relationship between the papers that have a tendency to extend or lower in relative significance / affect on this community over time? To discover this, utilizing R (see code in Appendix 1) we separated out the papers that had rising eigenvector centralities and people with reducing eigenvector centralities. Figures 6 and seven present the plots of the rising eigenvector centrality papers in pink and the reducing eigenvector centrality papers in blue. What unites these papers?
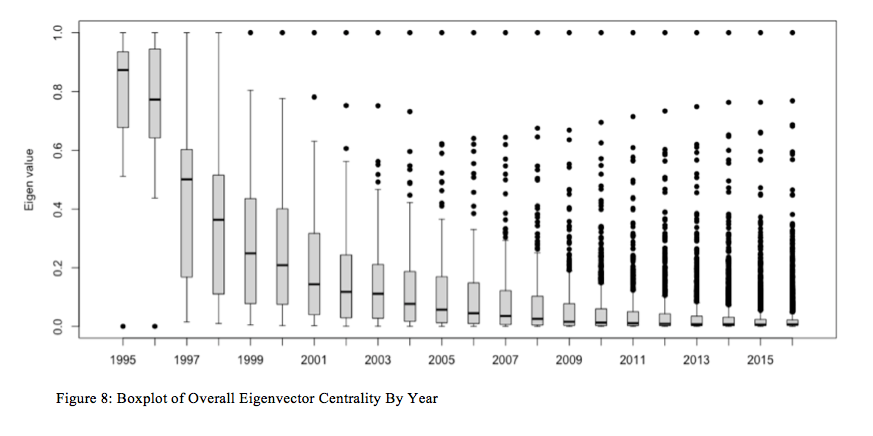
To realize a greater understanding of the general community pattern of eigenvector centrality for the papers in query, I made a decision to create a boxplot of all the paper eigenvector centralities for annually, which is represented in Fiugure 8. Determine 8, as soon as once more, exhibits a hanging consequence: whereas there definitely are some papers that grow to be way more essential, structurally, over time inside the community, the overwhelming majority of the papers are nearly inconsequential so far as eigenvector centrality goes. As an illustration, in 1995, the common eigenvector centrality rating was near .9 with a modest normal error; by 2001, it was lower than .2. As time progresses from 2001 by way of 2016, the common eigenvector centrality rating crashes to just about zero, whereas a handful of outliers develop of their structural significance inside the community. Who wrote these papers and what have been they about? Why and the way have they grow to be so structurally essential inside this community?
4.4 ERGM and the Evaluation of Micro-Stage Construction
One speculation could also be that native, or micro-level buildings might have an essential position to play within the structural evolution of this quotation community over time, thus inflicting sure papers/nodes inside the community to have a structural benefit over the others as the sector of information manufacturing expands. Right here I tried a modest ERGM evaluation (exponential random graph modeling). ERGM are a category of stochastic fashions which use community native buildings to mannequin the formation of community ties for a community with a set variety of nodes (Wang et al., 2009). They’re a helpful methodology that makes use of Markov Chain Most Chance Estimation to approximate estimates for the chances ratio of the presence of various micro-level buildings inside a community.
Desk 1 exhibits the outcomes of those modeling workouts on these NCD / international well being quotation networks as they evolve between 1995 and 2016. Whereas operating these fashions (which, it seems, takes a ton of time and computing energy) I realized that most of the community parameters that I had hoped to check inside this community (reminiscent of k-star, 4 cycles, triangles, and triad census) wouldn’t produce MCMC fashions that may converge. So, I used to be not in a position to estimate these parameters.
Nonetheless, I used to be in a position to estimate the ERGM parameters for the presence of edges, transitive triplets (ttriple), and density, and their values are present in Desk 1. The column labled ERGM~EDGES will be interpreted as a log odds measure of the density of the community. As may need anticipated based mostly on the evaluation of betweenness and closeness, in addition to the expansion of the variety of notes of the community, the log-odds of the likelihood of any tie (i.e. the density) crashes and begins to grow to be unfavourable beginning in 2001. The column labeled ERGM~DENSITY show an analogues pattern. The column labeled ERGM~TTRIPLE demonstrates a barely totally different pattern. It appears to begin modestly low (I couldn’t get the mannequin to run for 1995 knowledge, so it begins in 1996) after which appears to degree out at approximate zero, not changing into extra unfavourable or constructive because the community grows. This doubtlessly represents the relative lack of significance of transitive triplets within the micro construction of this community.
General, I’d be skeptical to make any grand claims concerning the utility of this ERGM evaluation. Though my MCMLE fashions appeared to converge, I used to be not in a position to run goodness of match analyses to check how properly these estimates match the mannequin and my precise networks. Moreover, ideally, I’d run these analyses on a quicker pc or achieve entry to a university-based tremendous pc since that is such a big knowledge set and I’m doing so many analyses with this time collection panel knowledge.
5) Dialogue
One clear puzzle emerges from this evaluation: whereas betweenness universally will increase for this community and closeness universally decreases, eigenvector centrality climbs for some papers and crashes for others. What’s extra, Determine 8’s boxplot overview of eigenvector centrality scores by yr exhibits that, on common, the papers are inconsequential to the general construction of the community and a handful of papers emerge to the highest as by far probably the most dominant. What are these papers and what would possibly it signify each for this as a website of scientific data and for the politics of worldwide well being precedence setting?
By analyzing the titles, abstracts, and authors of the papers which are most essential by way of eigenvector centrality and diploma, ten papers emerge as centrally essential:
- The European Group for Analysis and Therapy of Most cancers QLQ-C30: A High quality-of-Life Instrument for Use in Worldwide Scientific Trials in Oncology
- The MOS 36-Merchandise Brief Type Well being Survey (SF-36) 1. Conceptual Framework and Merchandise Choice
- Diagnostic and Statistical Handbook of Psychological Problems Supply Data (1994)
- Diagnostic and Statistical Handbook of Psychological Problems Supply Data (2000)
- Measurement of affected person consequence in arthritis
- Incapacity-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 illnesses and accidents in 21 areas, 1990–2010: a scientific evaluation for the International Burden of Illness Research 2010
- International and regional mortality from 235 causes of demise for 20 age teams in 1990 and 2010: a scientific evaluation for the International Burden of Illness Research 2010
- Statistical Energy Evaluation for the Behavioral Sciences
- Different projections of mortality and incapacity by trigger 1990–2020: International Burden of Illness Research
- A comparative threat evaluation of burden of illness and harm attributable to 67 threat elements and threat issue clusters in 21 areas, 1990–2010: a scientific evaluation for the International Burden of Illness Research 2010
There are a number of issues which are exceptional about this checklist of the (by far) most essential papers on this quotation community. First, apart from the primary most essential paper—which is concerning the medical strategy of diagnosing and treating most cancers—none of those items are a couple of particular illness and even class of illnesses. As an alternative, they’re all meta-analyses or statistical overviews of epidemiological tendencies in noncommunicable illnesses and their relative burdens globally. Second, the illness upon which they’re focusing tends to be biased in the direction of wealthy-world well being points: the DSM for psychological well being points (which has a extremely western-centric focus) and arthritis (has not been thought-about a rating international well being precedence). Lastly, all them must do with capturing international measurements, standardized practices and protocols, and dominant paradigms—constructed from applications and practices rooted within the U.S. and Europe—which are to function fashions for well being care techniques within the international south. Contemplating that this community, examined from 1995 by way of 2016 was about “international well being” and noncommunicable illnesses, it appears stunning that these can be the overwhelmingly dominant papers on this sparsely related community.
6) Conclusion
I started this paper with a commentary on the ways in which scientific quotation networks can allow and constrain the biopolitics of worldwide well being by reinforcing the legitimated framing of illnesses and their interventions in sure methods, and never others. This paper factors to the likelihood that the structural evolution of the NCD / international well being tutorial paper quotation community has contributed considerably to this biopolitical conundrum. Particularly, essential puzzle within the subject of worldwide well being is: why have non-communicable and continual illnesses been so dramatically marginalized inside the international well being precedence combine? First, evaluating the burden of noncommunicable illnesses (NCDs) and infectious illnesses to their relative magnitude of funding by way of improvement help for well being (DAH) demonstrates a exceptional disparity. Regardless of accounting for greater than 30% of the general illness burden globally (particularly in low and center earnings international locations), lower than 1% of all DAH is allotted particularly to care, therapy, and prevention of noncommunicable illness (Daniels, Donilon, & Bollyky, 2014).
Second, there was a concerted effort by the noncommunicable illness group of practitioners and students to boost the profile of NCDs on the worldwide stage (Geneau et al., 2010). A lot of this political and scientific labor has culminated in uncommon and extremely essential United Nations Basic Meeting Excessive Stage Assembly targeted on the worldwide burden of NCDs in 2011. This assembly was the primary UNGA Excessive Stage Assembly on a well being subject since HIV/AIDS in 2000. But, regardless of the eye from international leaders on the world stage, practically no new assets have been dedicated and invested in international NCD care and administration. Lastly, central to this debate has been a query concerning the nature of the social building of NCDs globally, particularly on the subject of the burden, causal sources, and crucial systems-level interventions to fulfill the burden. Main as much as the 2011 UNGA Excessive Stage Assembly on NCDs, the World Well being Group (WHO) has doubled down on a targeted framework of restricted shared “life-style modifiable” threat elements because the dominant causal supply of the NCDs globally. Dubbed the “4×4 Framework”, the WHO has sought to restrict the phrases of debate and focus to what they deem to be the 4 most “essential” NCDs and the corresponding particular person degree life-style modifiable dangers: most cancers, diabetes, cardio-vascular illness, and continual respiratory illness; tobacco use, unhealthy diets, bodily inactivity, and the dangerous use of alcohol (WHO, 2013). Students and practitioners, particularly these offering care in poor, distant areas of the world have taken goal at this framing, saying that it excludes a lot of the essential burden of sickness, particularly amongst the very poor and rural populations around the globe (Binagwaho, Muhimpundu, & Bukhman, 2014; Bukhman, Mocumbi, & Horton, 2015; Kwan et al., 2016; Bukhman et al., 2015).
These three interlocked challenges—the sheer disparity between NCDs / infectious illnesses’ assets and burden, the negligible progress in useful resource commitments regardless of NCDs’ expanded profile on the worldwide stage, and the dynamic scientific and political contest of NCDs’ social building and framing—create an attention-grabbing empirical puzzle that has essential implications for the politics and governance of worldwide well being. What is obstructing the political progress in increasing assets and tutorial give attention to a progressive technique for NCD care and management?
One speculation—that’s supported by the findings of this paper—is that the dominant NCD framing (particularly from the WHO and the worldwide scientific group) traditionally has been rooted in a North American / European-centric view: a slim set of sicknesses and their related individual-level, modifiable, statistically decided threat elements as the foundation causes (4×4 Framework). This framing has blocked the political momentum of NCDs as a result of 1) it situates the locus of trigger in unhealthy choices/behaviors of people and a pair of) it seems to be an sad byproduct of financial improvement and earnings progress. This framing renders the true expertise of the poorest and most marginalized invisible to international coverage makers and makes it tough for activists to demand new modes of financing to assist ministries of well being to construct progressive NCD therapy and prevention applications.
Works Cited
Airhihenbuwa, C. O., Ford, C. L., & Iwelunmor, J. I. (2014). Why tradition issues in well being interventions: classes from HIV/AIDS stigma and NCDs. Well being Educ Behav, 41(1), 78–84. [pii]
Babchuk, N., Keith, B., & Peters, G. (1999). Collaboration in sociology and different scientific disciplines: A comparative pattern evaluation of scholarship within the social, bodily, and mathematical sciences. The American Sociologist, 30(3), 5–21.
Binagwaho, A., Muhimpundu, M. A., & Bukhman, G. (2014). 80 underneath 40 by 2020: an fairness agenda for NCDs and accidents. The Lancet, 383(9911), 3–4.
Beaglehole, R., & Bonita, R. (2010). What’s international well being? International Well being Motion, 3(0), 1–2.
Brown, P. (1995). Naming and Framing: The Social Building of Analysis and Sickness. Journal of Well being and Social Conduct, 34–52.
Bukhman, G., Mocumbi, A. O., & Horton, R. (2015). Reframing NCDs and accidents for the poorest billion: a Lancet Fee. The Lancet, 386(10000), 1221–1222.
Bukhman, G., Bavuma, C., Gishoma, C., Gupta, N., Kwan, G. F., Laing, R., & Beran, D. (2015). Endemic diabetes on this planet’s poorest folks. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 3(6), 402–403.
Cappell, C. L., & Guterbock, T. M. (1992). Seen Schools: The Social and Conceptual Construction of Sociology Specialties. American Sociological Overview, 57(2), 266–273.
Conrad, P., & Barker, Ok. Ok. (2010). The social building of sickness: key insights and coverage implications. Journal of Well being and Social Conduct, 51(S), S67–S79.
Daipha, P. (2001). The mental and social group of ASA 1990–1997: Exploring the interface between the self-discipline of sociology and its practitioners. The American Sociologist, 32(3), 73–90.
Daniels, M. E., Donilon, T. E., & Bollyky, T. J. (2014). The Rising International Well being Disaster: Noncommunicable Ailments in Low- and Center-Revenue International locations. New York.
Fassin, D. (2012). That Obscure Object of International Well being. In Medical Anthropology on the Intersections: Histories, Activisms, and Futures, (p. 352).
Geneau, R., Stuckler, D., Stachenko, S., McKee, M., Ebrahim, S., Basu, S., …Beaglehole, R. (2010). Elevating the precedence of stopping continual illnesses: a political course of. The Lancet, 376(9753), 1689–1698. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61414-6
International Motion Plan for the Prevention and Management of Noncommunicable Ailments, 2013-2020. Rep. World Well being Group, 2013. Internet. <
Gondal, N. (2011). The native and international construction of information manufacturing in an emergent analysis subject: An exponential random graph evaluation. Social Networks, 33(1), 20–30.
Goyal, S., Van Der Leij, M. J., & Moraga‐González, J. L. (2006). Economics : An Rising Small World. The College of Chicago Press, 114(2), 403–412.
Hill, V., & Carley, Ok. M. (1999). An strategy to figuring out consensus in a subfield: The case of organizational tradition. Poetics, 27(1), 1–30.
Kaplan, N. (1965). The norms of quotation habits: Prolegomena to the footnote. American Documentation, 16(3), 179–184.
Katz, A. R. (2013). Noncommunicable illnesses: International well being precedence or market alternative? An illustration of the World Well being Group at its worst and at its finest. Worldwide Journal of Well being Companies, 43(3), 437–458.
Keane, C. (1998). Globality and Constructions of World Well being. Medical Anthropology Quarterly, 12(2), 226–240.
Kessler, M. M. (1963). Bibliographic coupling between scientific papers. American Documentation, 14(1), 10–25.
Kwan, G. F., Mayosi, B. M., Mocumbi, A. O., Miranda, J. J., Ezzati, M., Jain, Y., Bukhman, G. (2016). International Burden of Cardiovascular Illness Endemic Cardiovascular Ailments of the Poorest Billion.
Lantz, P. M., & Sales space, Ok. M. (1998). The social building of the breast most cancers epidemic. Social Science and Medication, 46(7), 907–918.
Lievrouw, L., Rogers, E.M., Lowe, C.U., Nadel, E., 1987. Triangulation as analysis technique for figuring out invisible schools amongst biomedical scientists. Social Networks 9 (3), 217–248.
Mamudu, H. M., Yang, J. S., & Novotny, T. E. (2011). UN decision on the prevention and management of non-communicable illnesses: a chance for international motion. International Public Well being, 6(4), 347–353.
Moody, J., & Mild, R. (2006). A view from above: The evolving sociological panorama. American Sociologist, 37(2), 67–86.
Newman, M. E. J. The arithmetic of networks. Middle for the Research of Complicated Methods, College of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Small, H., & Griffith, B. C. (1974). The Construction of Scientific Literatures I : Figuring out and Graphing Specialties Creator ( s ): Henry Small and Belver C . Griffith Revealed by : Sage Publications , Ltd . Steady URL : REFERENCES Linked references are av. Science Research, 4(1), 17–40.
Šubelj, L., Fiala, D., & Bajec, M. (2014). Community-based statistical comparability of quotation topology of bibliographic databases. Scientific Studies, 4, 6496.
Wang, P., Sharpe, Ok., Robins, G. L., & Pattison, P. E. (2009). Exponential random graph (p *) fashions for affiliation networks. Social Networks, 31(1), 12–25.
Wasserman, Stanley; Faust, Katherine (1994). Social Community Evaluation: Strategies and Functions (Structural Evaluation within the Social Sciences) (p. 188). Cambridge College Press. Kindle Version.
Whyte, S. R. (2012). Chronicity and management: framing “noncommunicable illnesses” in Africa. Anthropology & Medication, 19(1), 63–74.
Source link
